The Relationship between Insulin-dependent Diabetes Mellitus (Type 1 Diabetes) and Dental Caries: A Meta-Analysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10701672Keywords:
dental caries, insulin dependent diabetes, type 1 diabetes mellitus, meta-analysisAbstract
Objectives The objective of this study was to perform a meta-analysis by combining the findings of studies that examined the link between insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) and dental caries in both permanent as well as deciduous teeth.
Materials and Methods The PRISMA statement guide was utilized in order to conduct a thorough meta-analysis. This involved conducting searches across electronic databases to select relevant studies, as well as collecting pertinent data. A comprehensive evaluation of biases was also performed, both on an individual and collective level. For the purposes of comparing results, mean differences (MD) were implemented as the primary metric for measuring effect estimates.
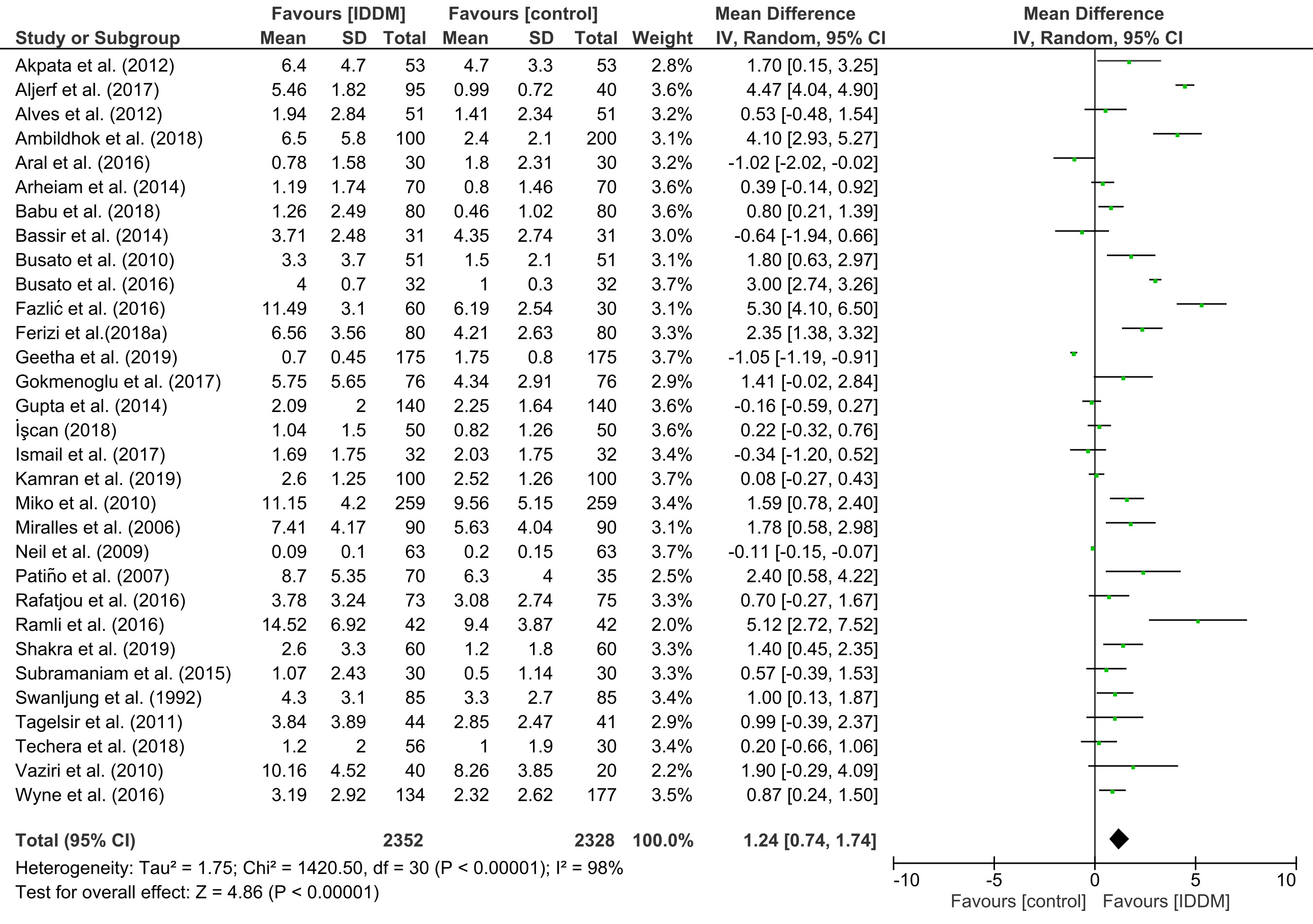
Results The study consisted of 42 qualitative and 32 quantitative analyses. The DMFT score was significantly higher in the IDDM group compared to the control group (MD=1.24, CI:0.74,1.74;p<0.001), but there was no significant difference in the dmft score (MD=-0.40, 95%CI:-0.82,0.02;p=0.06). The statistical outcomes for DMFT (Tau2=1.75, Chi2=1420.50, I2=98%, p<0.001) and dmft (Tau2=0.36, Chi2=75.01, I2=84%, p<0.001) showed considerable heterogeneity.
Conclusions Research suggests that individuals with IDDM may have an increased risk of developing dental caries in their permanent teeth. However, this association between IDDM and dental caries does not appear to be present in deciduous teeth.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Tanvi Shah, Surendar Sugumaran, Astha Mehta

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
CC Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0








